Industrial Communication
We offer a selected range of hardware from various manufacturers to build your robust and reliable IIoT communication.
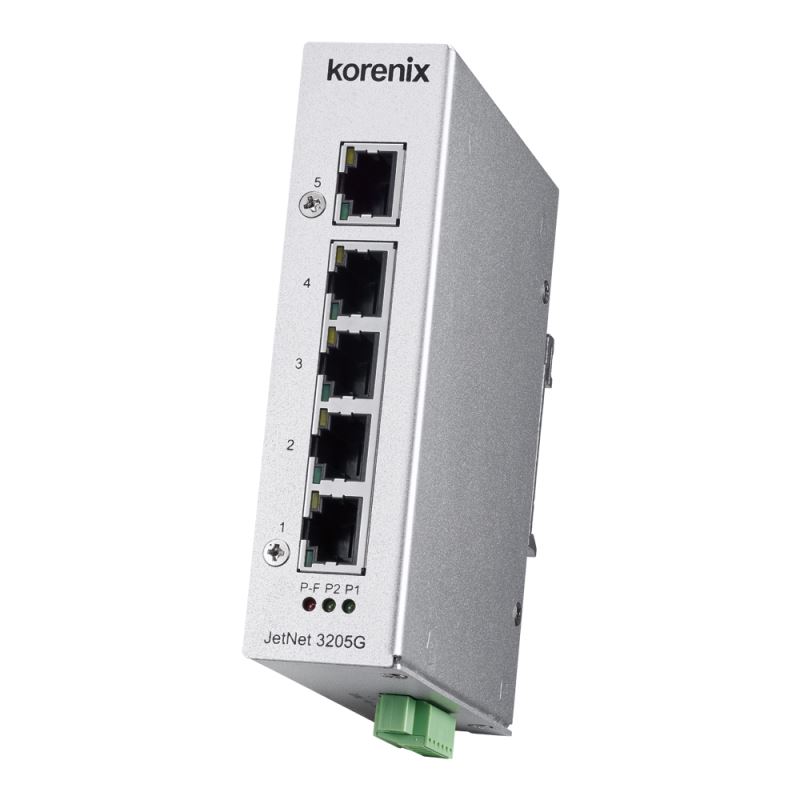
Switches
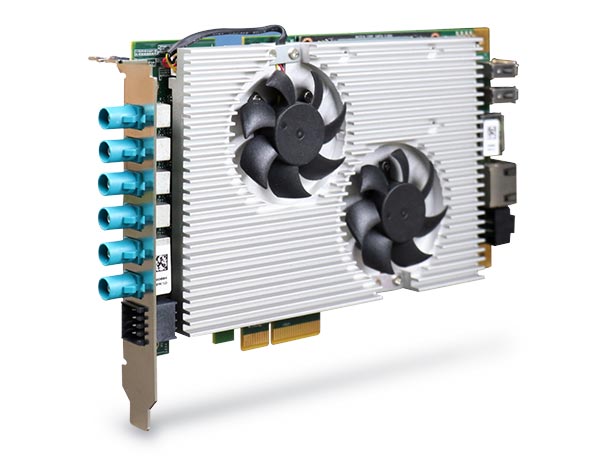
Framegrabber cards
A brief history of industrial communication technologies from the simple relay to the 5G standard:
The beginnings
Communication between machines was initially limited to direct, physical connections such as cables and relays that transmitted signals from one point to another. Telephone lines and later digital communication technologies improved flexibility and efficiency in industrial production.
The introduction of the first fieldbus systems marked a turning point in the 1970s and 1980s. These enabled communication between several devices via a single cable. Fieldbus systems significantly reduced the complexity and cost of cabling. Protocols such as Modbus and later Profibus standardised communication between devices from different manufacturers.
The state of the art today
Today, the seamless transfer of data between devices is based on a variety of technologies and standards. Modern industrial networks use both wired and wireless technologies, including Ethernet-based protocols such as Profinet and EtherCAT, which are optimised for high speed and real-time capability. These networks also support the integration of sensors and actuators.
The introduction of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) enables the networking of machines and systems via the internet. This allows centralised monitoring and control of processes as well as the use of cloud technologies for data storage and analysis. The connection of production facilities with IT systems optimises production processes and predicts maintenance requirements (‘predictive maintenance’).
A look into the future
Technologies such as 5G offer the potential for even more flexible network solutions for real-time data transmission, even in mobile or inaccessible environments. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will support the analysis of data directly at the point of origin (edge computing) and thus enable faster decision-making processes.
Increasing networking in industry is associated with an increasing risk of cyberattacks. Security in industrial networks is a key challenge.
Nevertheless, industrial communication is moving towards an increasingly networked, intelligent and flexible manufacturing environment. These are the foundations of Industry 4.0 and beyond.